By: Dr Alexia Farrugia, Dr Rebecca Preston
Guy’s & St. Thomas’ NHS Trust, London
A 70 year old lady presents with shortness of breath. A chest X-ray revealed deviation of the thyroid gland to the right secondary due to a predominantly left-sided anterior mediastinal mass. CT thorax revealed a thyroid goitre. A thyroidectomy was performed and histology revealed follicular thyroid carcinoma. In view of the relatively de-differentiated tumour, radioiodine ablation was done.
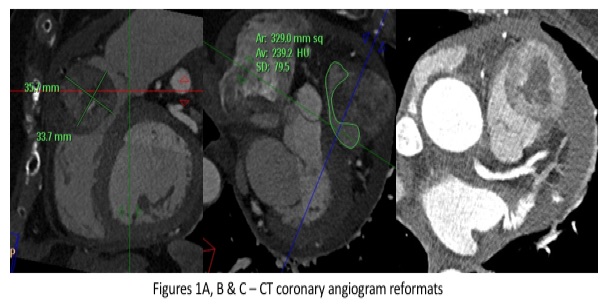
Two years later, the patient was noted on biochemical results to have a high serum calcium level and a rising thyroglobulin. FDG PET-CT was performed showing new focal increased tracer uptake posterior to the left thyroid bed and adjacent to the oesophagus. Also, there was a further focus of increased tracer uptake related to the right ventricle and pulmonary trunk. Appearances were in keeping with local recurrence within the left thyroid bed and an indeterminate new focal uptake within the right ventricle and pulmonary trunk. An urgent fine needle aspiration of the left thyroid nodule was performed and follicular thyroid carcinoma recurrence was confirmed on histology. A CT coronary angiogram revealed a soft-tissue mass anterior to and invading the pulmonary outflow tract and was seen to involve the anterior pericardium. A new pericardial effusion was noted. (Figure).
CT-guided biopsy of the anterior mediastinal mass was performed. Histology revealed round cells strongly positive for TTF-1 and thyroglobulin. Given the histological morphological features and immuno-histochemical profile of the biopsy specimen was consistent with metastatic disease from the known thyroid primary. Neck dissection was performed to excise the suspicious foci of recurrence within the thyroid bed.
Multiple choice questions
1. Which is the most common site of metastatic deposits from thyroid carcinoma?
- Cardiac / valvular
- Cervical lymph nodes
- Lung parenchyma
- Osseous
- Hepatic
2. Which is the commonest type of thyroid malignancy?
- Papillary
- Follicular
- Anaplastic
- Medullary
- Lymphoma
3. Which are the commonest tumours to metastasise to the heart?
- Pleural mesothelioma
- Melanoma
- Lung adenocarcinoma
- Breast carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
Figures 1A, B & C – CT coronary angiogram reformats. Sagittal, coronal and axial CT coronary angiogram images demonstrating a peripherally-enhancing, centrally necrotic mass within the pulmonary outflow tract, with a moderately-sized pericardial effusion.
Figures 2A & B – 18-F FDG PET-CT images. FDG PET-CT uptake is present within the right ventricular outflow tract and within the left thyroid bed consistent with a metastatic deposit and recurrence of follicular thyroid carcinoma respectively.
Images courtesy of: Guy’s & St Thomas’ NHS Trust & PET Centre at St Thomas’ Hospital, London
Answers: 1=b, 2=b, 3=a.